1.What are the principle concepts of OOPS?
There are four principle concepts upon which object oriented design and programming rest.
They are:
- Abstraction
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance
- Encapsulation
(i.e. easily remembered as A-PIE).
2.What is Abstraction?
Abstraction refers to the act of representing essential features without including the background details or explanations.
Abstraction is nothing but data hiding . In java we will provide the object to users then they will use the object's but they doesn't know what is happening the behind .
Abstraction is nothing but data hiding . In java we will provide the object to users then they will use the object's but they doesn't know what is happening the behind .
3.What is Encapsulation?
Encapsulation is a technique used for hiding the properties and behaviors of an object and allowing outside access only as appropriate. It prevents other objects from directly altering or accessing the properties or methods of the encapsulated object.
4.What is the difference between abstraction and encapsulation?
- Abstraction focuses on the outside view of an object (i.e. the interface) Encapsulation (information hiding) prevents clients from seeing it’s inside view, where the behavior of the abstraction is implemented.
- Abstraction solves the problem in the design side while Encapsulation is the Implementation.
- Encapsulation is the deliverables of Abstraction. Encapsulation barely talks about grouping up your abstraction to suit the developer needs.
5.What is Inheritance?
- Inheritance is the process by which objects of one class acquire the properties of objects of another class.
- A class that is inherited is called a superclass.
- The class that does the inheriting is called a subclass.
- Inheritance is done by using the keyword extends.
- The two most common reasons to use inheritance are:
- To promote code reuse
- To use polymorphism
6.What is Polymorphism?
Polymorphism is briefly described as "one interface, many implementations." Polymorphism is a characteristic of being able to assign a different meaning or usage to something in different contexts - specifically, to allow an entity such as a variable, a function, or an object to have more than one form.
7.How does Java implement polymorphism?
(Inheritance, Overloading and Overriding are used to achieve Polymorphism in java).
Polymorphism manifests itself in Java in the form of multiple methods having the same name.
Polymorphism manifests itself in Java in the form of multiple methods having the same name.
- In some cases, multiple methods have the same name, but different formal argument lists (overloaded methods).
- In other cases, multiple methods have the same name, same return type, and same formal argument list (overridden methods).
8.Explain the different forms of Polymorphism.
There are two types of polymorphism one is Compile time polymorphism and the other is run time polymorphism. Compile time polymorphism is method overloading. Runtime time polymorphism is done using inheritance and interface.
Note: From a practical programming viewpoint, polymorphism manifests itself in three distinct forms in Java:
Note: From a practical programming viewpoint, polymorphism manifests itself in three distinct forms in Java:
- Method overloading
- Method overriding through inheritance
- Method overriding through the Java interface
9.What is runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch?
In Java, runtime polymorphism or dynamic method dispatch is a process in which a call to an overridden method is resolved at runtime rather than at compile-time. In this process, an overridden method is called through the reference variable of a superclass. The determination of the method to be called is based on the object being referred to by the reference variable.
10.What is Dynamic Binding?
Binding refers to the linking of a procedure call to the code to be executed in response to the call. Dynamic binding (also known as late binding) means that the code associated with a given procedure call is not known until the time of the call at run-time. It is associated with polymorphism and inheritance.
11.What is method overloading?
Method Overloading means to have two or more methods with same name in the same class with different arguments. The benefit of method overloading is that it allows you to implement methods that support the same semantic operation but differ by argument number or type.
Note:
Note:
- Overloaded methods MUST change the argument list
- Overloaded methods CAN change the return type
- Overloaded methods CAN change the access modifier
- Overloaded methods CAN declare new or broader checked exceptions
- A method can be overloaded in the same class or in a subclass
12.What is method overriding?
Method overriding occurs when sub class declares a method that has the same type arguments as a method declared by one of its superclass. The key benefit of overriding is the ability to define behavior that’s specific to a particular subclass type.
Note:
Note:
- The overriding method cannot have a more restrictive access modifier than the method being overridden (Ex: You can’t override a method marked public and make it protected).
- You cannot override a method marked final
- You cannot override a method marked static
13. Differentiate between method overloading and method overriding.
You overload by adding multiple method definitions (same name, but different argument lists). You override by changing the definition of a base class' method (polymorphism).
You overload by adding multiple method definitions (same name, but different argument lists). You override by changing the definition of a base class' method (polymorphism).
14.Can overloaded methods be override too?
Yes, derived classes still can override the overloaded methods. Polymorphism can still happen. Compiler will not binding the method calls since it is overloaded, because it might be overridden now or in the future.
15.Is it possible to override the main method?
NO, because main is a static method. A static method can't be overridden in Java.
16.How to invoke a superclass version of an Overridden method?
To invoke a superclass method that has been overridden in a subclass, you must either call the method directly through a superclass instance, or use the super prefix in the subclass itself. From the point of the view of the subclass, the super prefix provides an explicit reference to the superclass' implementation of the method.
// From subclass
super.overriddenMethod();
17.What is super?
super is a keyword which is used to access the method or member variables from the superclass. If a method hides one of the member variables in its superclass, the method can refer to the hidden variable through the use of the super keyword. In the same way, if a method overrides one of the methods in its superclass, the method can invoke the overridden method through the use of the super keyword.
Note:
Note:
- You can only go back one level.
- In the constructor, if you use super(), it must be the very first line of code.
18.How do you prevent a method from being overridden?
To prevent a specific method from being overridden in a subclass, use the final modifier on the method declaration, which means "this is the final implementation of this method", the end of its inheritance hierarchy.
public final void exampleMethod() {
// Method statements
}
// Method statements
}
19.What is an Interface?
An interface is a description of a set of methods that conforming implementing classes must have.
Note:
Note:
- You can’t mark an interface as final.
- Interface variables must be static.
- An Interface cannot extend anything but another interfaces.
20.Can we instantiate an interface?
You can’t instantiate an interface directly, but you can instantiate a class that implements an interface.
21.Can we create an object for an interface?
Yes, it is always necessary to create an object implementation for an interface. Interfaces cannot be instantiated in their own right, so you must write a class that implements the interface and fulfill all the methods defined in it.
22.Do interfaces have member variables?
Interfaces may have member variables, but these are implicitly public, static,and final- i.e,
interfaces can declare only constants, not instance variables that are available to all implementations and may be used as key references for method arguments for example.
interfaces can declare only constants, not instance variables that are available to all implementations and may be used as key references for method arguments for example.
23.What modifiers are allowed for methods in an Interface?
Only public and abstract (default) modifiers are allowed for methods in interfaces.
24.What is a marker interface?
Marker interfaces are those which do not declare any required methods, but signify their compatibility with certain operations. The java.io.Serializable interface and Cloneable are typical marker interfaces. These do not contain any methods, but classes must implement this interface in order to be serialized and de-serialized.
25.What is an abstract class?
Abstract classes are classes that contain one or more abstract methods. An abstract method is a method that is declared, but contains no implementation.
Note:
Note:
- If even a single method is abstract, the whole class must be declared abstract.
- Abstract classes may not be instantiated, and require subclasses to provide implementations for the abstract methods.
- You can’t mark a class as both abstract and final.
26.Can we instantiate an abstract class?
An abstract class can never be instantiated. Its sole purpose is to be extended (subclassed).
27.What are the differences between Interface and Abstract class?
When To Use Interfaces:
An interface allows somebody to start from scratch to implement your interface or implement your interface in some other code whose original or primary purpose was quite different from your interface. To them, your interface is only incidental, something that have to add on to the their code to be able to use your package.
When To Use Abstract classes:
An abstract class, in contrast, provides more structure. It usually defines some default implementations and provides some tools useful for a full implementation. The catch is, code using it must use your class as the base. That may be highly inconvenient if the other programmers wanting to use your package have already developed their own class hierarchy independently. In Java, a class can inherit from only one base class.
28. Can I use both abstract classes and interfaces?
You can offer the best of both worlds, an interface and an abstract class. Implementors can ignore your abstract class if they choose. The only drawback of doing that is calling methods via their interface name is slightly slower than calling them via their abstract class name.
29.When you declare a method as abstract, can other non abstract methods access it?
Yes, other non abstract methods can access a method that you declare as abstract.
30.Can there be an abstract class with no abstract methods in it?
Yes, there can be an abstract class without abstract methods.
But an abstract class without any abstract methods should be a rare thing and you should always question your application design if this case arises. Normally you should refactor to use a concrete superclass in this scenario.
But an abstract class without any abstract methods should be a rare thing and you should always question your application design if this case arises. Normally you should refactor to use a concrete superclass in this scenario.
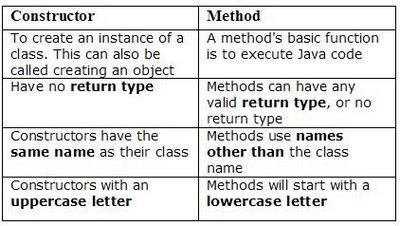
31.What is Constructor?
- A constructor is a special method whose task is to initialize the object of its class.
- It is special because its name is the same as the class name.
- They do not have return types, not even void and therefore they cannot return values.
- They cannot be inherited, though a derived class can call the base class constructor.
- Constructor is invoked whenever an object of its associated class is created.
32.How does the Java default constructor be provided?
If a class defined by the code does not have any constructor, compiler will automatically provide one no-parameter-constructor (default-constructor) for the class in the byte code. The access modifier (public/private) of the default constructor is the same as the class itself.
33.Can constructor be inherited?
No, constructor cannot be inherited, though a derived class can call the base class constructor.
- Constructors use this to refer to another constructor in the same class with a different parameter list.
- Constructors use super to invoke the superclass's constructor. If a constructor uses super, it must use it in the first line; otherwise, the compiler will give an error.
36.What are the differences between Class Methods and Instance Methods?
To understand the difference between a class method and an instance method, we need to go back to the distinction of class and object. Remember that a class is a definition while an object is an instance of that definition.
Class methods are methods which are declared as static. The method can be called without creating an instance of the class. Class methods can only operate on class members and not on instance members as class methods are unaware of instance members.
Instance methods on the other hand require an instance of the class to exist before they can be called, so an instance of a class needs to be created by using the new keyword. Instance methods operate on specific instances of classes. Instance methods of the class can also not be called from within a class method unless they are being called on an instance of that class. Instance methods are not declared as static.
37.How are this() and super() used with constructors?
- Constructors use this to refer to another constructor in the same class with a different parameter list.
- Constructors use super to invoke the superclass's constructor. If a constructor uses super, it must use it in the first line; otherwise, the compiler will complain.
38.What are Access Specifiers?
One of the techniques in object-oriented programming is encapsulation. It concerns the hiding of data in a class and making this class available only through methods. Java allows you to control access to classes, methods, and fields via the access specifiers.
39.What are Access Specifiers available in Java?
Java offers four access specifiers, listed below in decreasing accessibility:
- Public- public classes, methods, and fields can be accessed from everywhere.
- Protected- protected methods and fields can only be accessed within the same class to which the methods and fields belong, within its subclasses, and within classes of the same package.
- Default(no specifier)- If you do not set access to specific level, then such a class, method, or field will be accessible from inside the same package to which the class, method, or field belongs, but not from outside this package.
- Private- private methods and fields can only be accessed within the same class to which the methods and fields belong. private methods and fields are not visible within subclasses and are not inherited by subclasses.
40.What is final modifier?
The final modifier keyword makes that the programmer cannot change the value anymore. The actual meaning depends on whether it is applied to a class, a variable, or a method.
- final Classes- A final class cannot have subclasses.
- final Variables- A final variable cannot be changed once it is initialized.
- final Methods- A final method cannot be overridden by subclasses.
41.What are the uses of final method?
There are two reasons for marking a method as final:
- Disallowing subclasses to change the meaning of the method.
- Increasing efficiency by allowing the compiler to turn calls to the method into inline Java code.
42.What is static block?
Static block which exactly executed exactly once when the class is first loaded into JVM. Before going to the main method the static block will execute.
43.What are static variables?
Variables that have only one copy per class are known as static variables. They are not attached to a particular instance of a class but rather belong to a class as a whole. They are declared by using the static keyword as a modifier.
static type varIdentifier;
where, the name of the variable is varIdentifier and its data type is specified by type.
Note: Static variables that are not explicitly initialized in the code are automatically initialized with a default value. The default value depends on the data type of the variables.
Note: Static variables that are not explicitly initialized in the code are automatically initialized with a default value. The default value depends on the data type of the variables.
44.What is the difference between static and non-static variables?
A static variable is associated with the class as a whole rather than with specific instances of a class. Non-static variables take on unique values with each object instance.
45.What are static methods?
Methods declared with the keyword static as the modifier are called static methods or class methods. They are so called because they affect a class as a whole, not a particular instance of the class. Static methods are always invoked without reference to a particular instance of a class.
Note: The use of a static method suffers from the following restrictions:
Note: The use of a static method suffers from the following restrictions:
- A static method can only call other static methods.
- A static method must only access static data.
- A static method cannot reference to the current object using keywords super or this.
46. What is the performance impact of the StringBuffer and String classes?
Java provides the StringBuffer and String classes, and the String class is used to manipulate character strings that cannot be changed. Simply stated, objects of type String are read only and immutable. The StringBuffer class is used to represent characters that can be modified.
The significant performance difference between these two classes is that StringBuffer is faster than String when performing simple concatenations.
In String manipulation code, character strings are routinely concatenated. Using the String class, concatenations are typically performed as follows:
String str = new String ("Stanford "); str += "Lost!!";
If you were to use StringBuffer to perform the same concatenation, you would need code that looks like this: StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer ("Stanford "); str.append("Lost!!");
Developers usually assume that the first example above is more efficient because they think that the second example, which uses the append method for concatenation, is more costly than the first example, which uses the + operator to concatenate two Stringobjects.
The + operator appears innocent, but the code generated produces some surprises. Using a StringBuffer for concatenation can in fact produce code that is significantly faster than using a String.
46. What are Checked and Unchecked Exceptions?
Java classifies all exceptions as either checked or unchecked. During compilation, the compiler checks each method (including constructor methods) to see whether it throws checked exceptions. If so, that method must include a Throws clause that lists each checked exception's class name. If that is not done, the compiler reports an error. Objects created from Exception and all of its subclasses (apart from RuntimeException and its subclasses) represent checked exceptions.Java provides the StringBuffer and String classes, and the String class is used to manipulate character strings that cannot be changed. Simply stated, objects of type String are read only and immutable. The StringBuffer class is used to represent characters that can be modified.
The significant performance difference between these two classes is that StringBuffer is faster than String when performing simple concatenations.
In String manipulation code, character strings are routinely concatenated. Using the String class, concatenations are typically performed as follows:
String str = new String ("Stanford "); str += "Lost!!";
If you were to use StringBuffer to perform the same concatenation, you would need code that looks like this: StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer ("Stanford "); str.append("Lost!!");
Developers usually assume that the first example above is more efficient because they think that the second example, which uses the append method for concatenation, is more costly than the first example, which uses the + operator to concatenate two Stringobjects.
The + operator appears innocent, but the code generated produces some surprises. Using a StringBuffer for concatenation can in fact produce code that is significantly faster than using a String.
46. What are Checked and Unchecked Exceptions?
Unchecked exceptions are based on either a flaw in the program's logic or a JVM failure.
Examples:
- Attempting to divide an integer by zero,
- Attempting to access an array element using a bad index,
- Attempting to create an array with a negative number of elements,
- Attempting to pass an invalid argument to a method,
- Unable to find a class file,
- Running out of memory,
- A badly formatted class file.